Abstract
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is an aggressive hematologic malignancy of plasmacytoid dendritic precursor cells. Lacking standard therapy due to limited understanding of biology and historical rarity of the disease, clinical outcomes for BPDCN patients remain poor. Surface overexpression of CD123/IL3Rα is seen 70-80% of patients with AML (Han et.al, Clin Cancer Res, 2017) and in nearly 100% of BPDCN cases, with a markedly high intensity compared to normal hematopoietic stem cells, thus making CD123 an attractive target for BPDCN treatment.
IMGN632 is a CD123-targeting antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) comprised of a novel humanized anti-CD123 antibody G4723A linked to a DNA mono-alkylating payload of the indolindobenzodiazepine pseudodimer (IGN) class of cytotoxic compounds. IMGN632 demonstrates potent activity in AML samples at low concentrations with minimal impact on normal bone marrow progenitors, and anti-leukemia effects in AML xenograft models (Kovtun et.al., Blood Advances, 2018). A phase I clinical trial of IMGN632 in relapse/ refractory AML (NCT033865) is now being performed and achieved encouraging results. We thus explored the anti-tumor effect of IMGN632 in BPDCN.
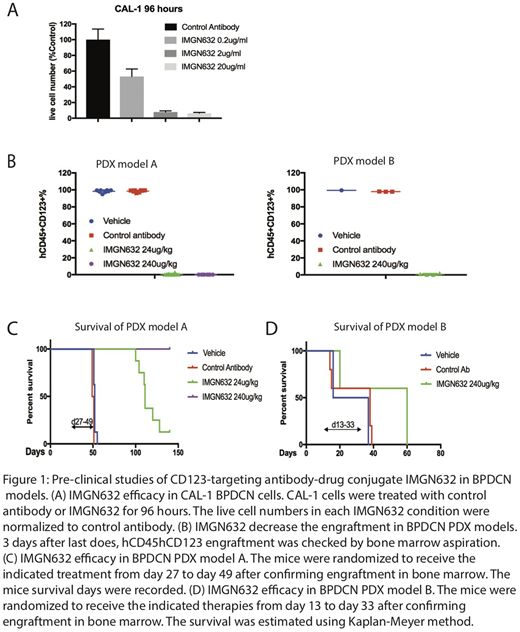
We first tested the in vitro activity of IMGN632 in a BPDCN cell line CAL-1. Cells were exposed to control antibody or IMGN632 at various concentration for 96 hours, after which viable cell numbers were measured using AnnexinV /DAPI assay with counting beads by flow cytometry. IMGN632 demonstrated cytotoxic activity at 0.2μg/ml, with stronger effects at concentrations of 2μg/ml and above (Figure 1A).
Next, the in vivo efficacy of IMGN632 was evaluated in BPDCN patient-derived-xenograft (PDX) models. NSG mice (6-8 weeks old) were injected with 1e6/mouse BPDCN cells by tail vein 24 hours after 250cGY sublethal irradiation. Upon confirmation of the bone marrow engraftment of hCD45/hCD123 cells by bone marrow aspiration, mice were randomized to 5 or 8 mice/group and received weekly intravenous vehicle, control antibody or IMGN632 by tail vein injection 24 hours following FcR blockade (400mg/kg naked antibody by intraperitoneal injection) for 3 weeks. Bone marrow engraftment and survival were monitored.
For model A, the mice received either 24μg/kg or 240μg/kg of IMGN632. For model B, the mice received 240μg/kg IMGN632. Both samples responded to the IMGN632 treatment, with the engraftment lower than 1% in the bone marrow after 3 doses, compared with over 90% in vehicle and control antibody group (Figure 1B). All mice from vehicle and control antibody groups in model A died by 52 days after cell injection; the 24μg/kg IMGN632 treated mice had prolonged survival with median survival of 111 days (p<0.0001), and the 240μg/kg IMGN632 treated mice are still alive after more than 140 days (p<0.0001) (Figure 1C). In the aggressive model B, a fraction of mice in each group died before efficacy could be established; the rest of the mice survived a median of 39 days in the control arm and 60 days in IMGN632-treated animals (p=0.0343) (Figure 1D). No evidence of treatment-related toxicity was observed using murine weight as a read-out.
In summary, our preliminary data demonstrate pre-clinical proof of targeting CD123 in BPDCN using a novel antibody-drug conjugate. IMGN632 exhibited promising anti-tumor effects in BPDCN in vitro and in vivo, even at a dose 10-fold lower than the anticipated therapeutically active dose. This large therapeutic window would be expected to be advantageous when used in combination with other treatments in BPDCN.
Adams:ImmunoGen Inc.: Employment. Callum:ImmunoGen Inc.: Employment. Lane:Stemline Therapeutics: Research Funding; N-of-one: Consultancy. Kovtun:ImmunoGen Inc.: Employment. Daver:Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; BMS: Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding; Otsuka: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Alexion: Consultancy; Sunesis: Consultancy; Pfizer: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; ImmunoGen: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Research Funding. Pemmaraju:Affymetrix: Research Funding; SagerStrong Foundation: Research Funding; plexxikon: Research Funding; daiichi sankyo: Research Funding; samus: Research Funding; celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; abbvie: Research Funding; cellectis: Research Funding; stemline: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; novartis: Research Funding. McKay:ImmunoGen Inc.: Employment. Konopleva:Stemline Therapeutics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal